
Wiki pic - Graphical example of insertion sort. Source.
Iterative Insertion Sort
function insertionSortIterative(arr) {
const len = arr.length
for (let i = 1; i < len; i++) {
const ith = arr[i]
let j = i - 1
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > ith) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j]
j--
}
arr[j + 1] = ith
}
return
}
/*
Time Complexity:
Average and Worse Case: O(n^2)
Best Case: O(n)
Space complexity - O(1)
*/
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
const testCases = [
[
[5, 4, 3, 2, 1],
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
],
[
[5, 6, 1, 0, 6, 2],
[0, 1, 2, 5, 6, 6],
],
[
[-1, 6, 2, 100, 0, -11],
[-11, -1, 0, 2, 6, 100],
],
]
for (const test of testCases) {
insertionSortIterative(test[0])
console.log(JSON.stringify(test[0]) === JSON.stringify(test[1]))
}Recursive Insertion Sort
// Recursive insertion sort with shifting of elements.
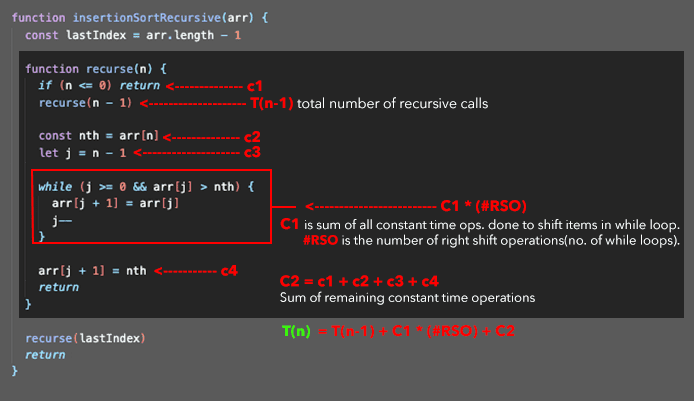
function insertionSortRecursive(arr) {
const lastIndex = arr.length - 1
function recurse(n) {
if (n <= 0) return
recurse(n - 1)
// Hold the value to be inserted in nth
const nth = arr[n]
// Starting at n - 1, until arr[j] < nth, keep shifting arr[j] to the right
let j = n - 1
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > nth) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j]
j--
}
// Place nth in correct position
arr[j + 1] = nth
return
}
recurse(lastIndex)
return
}
/*
Time Complexity:
Average and Worse Case: O(n^2)
Best Case: O(n)
Space complexity - O(n) (stack size)
*/
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
const testCases = [
[
[5, 4, 3, 2, 1],
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
],
[
[5, 6, 1, 0, 6, 2],
[0, 1, 2, 5, 6, 6],
],
[
[-1, 6, 2, 100, 0, -11],
[-11, -1, 0, 2, 6, 100],
],
]
for (const test of testCases) {
insertionSortRecursive(test[0])
console.log(JSON.stringify(test[0]) === JSON.stringify(test[1]))
}Calculating the Time Complexity of Recursive Insertion Sort
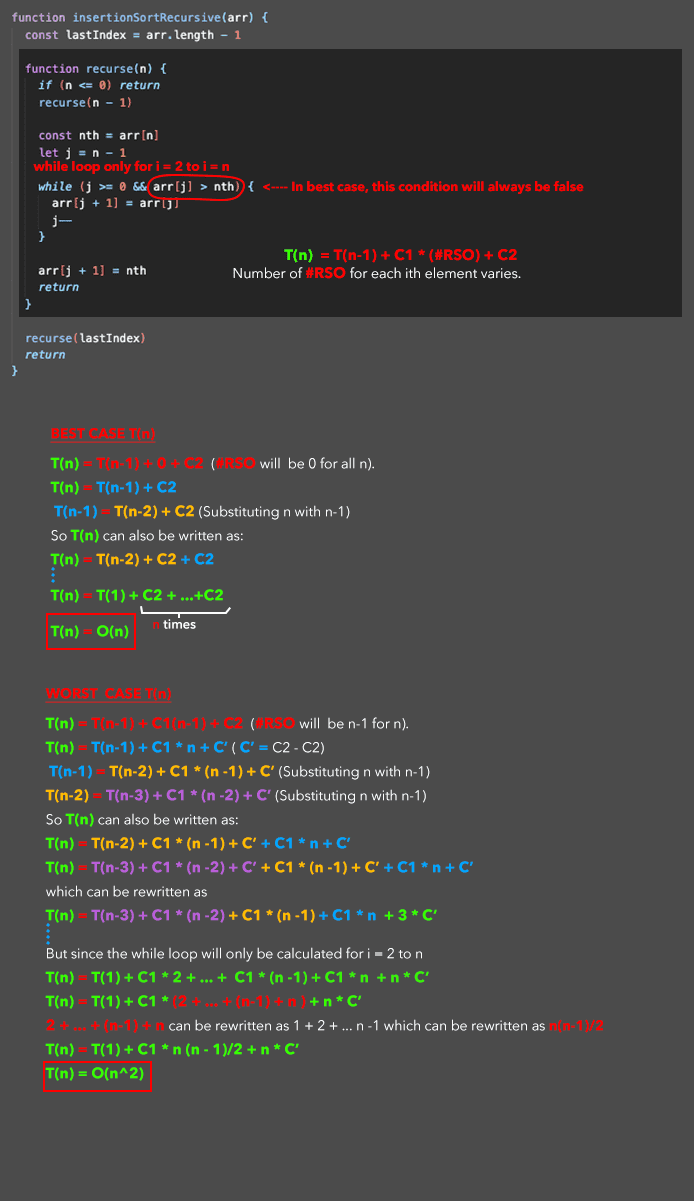
There is another way to implement recursive insertion sort - with repeated swaps to 'bubble up' the nth element.
function insertionSortRecursiveBubble(arr) {
const lastIndex = arr.length - 1
function recurse(n) {
// base case
if (n <= 0) return
// recurse on n - 1
recurse(n - 1)
// Bubble up and insert nth item in its place
let j = n
while (j >= 1 && arr[j - 1] > arr[j]) {
swap(arr, j - 1, j)
j--
}
return
}
recurse(lastIndex)
return
}
function swap(array, i, j) {
let temp = array[i]
array[i] = array[j]
array[j] = temp
}